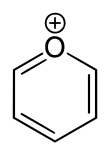
Pyrylium
Pyrylium cations react with nucleophiles at the ortho and para positions, typically through ANRORC.
In warm deuterium oxide, 2,4,6-trimethylpyrylium salts undergo isotopic exchange of 4-methyl hydrogens faster than for the 2- and 6-methyl groups, allowing the synthesis of regioselectively deuterated compounds.
[citation needed] Pyrylium's electrophilicity makes them useful materials for producing other compounds with stronger aromatic character.
Many important cations are formally derived from pyrylium by substitution of various functional groups for some or all the hydrogens in the ring.
A pyrylium cation with a hydroxyl anion substituent in the 2-position is not the zwitterionic aromatic compound (1), but the neutral unsaturated lactone 2-pyrone or pyran-2-one (2).
A class of flavylium-derived compounds are anthocyanidins and anthocyanins, pigments that are responsible for the colors of many flowers.