Quasi-Zenith Satellite System
[1] The goal of QZSS is to provide highly precise and stable positioning services in the Asia-Oceania region, compatible with GPS.
[2] Four-satellite QZSS services were available on a trial basis as of 12 January 2018,[3] and officially started on 1 November 2018.
A contract was awarded to Advanced Space Business Corporation (ASBC), that began concept development work, and Mitsubishi Electric, Hitachi, and GNSS Technologies Inc.
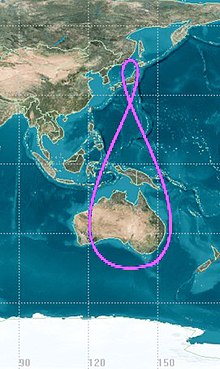
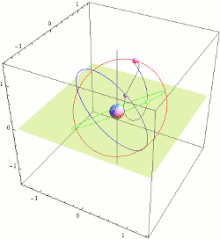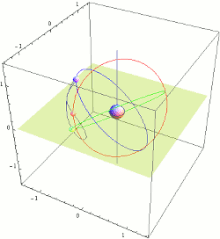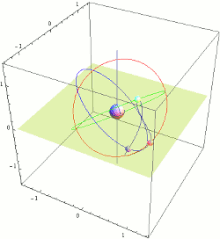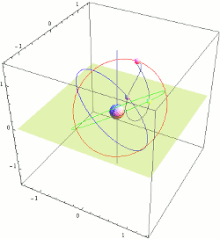
Instead, their ground traces are asymmetrical figure-8 patterns (analemmas), designed to ensure that one is almost directly overhead (elevation 60° or more) over Japan at all times.
[17] The primary purpose of QZSS is to increase the availability of GPS in Japan's numerous urban canyons, where only satellites at very high elevation can be seen.
A secondary function is performance enhancement, increasing the accuracy and reliability of GPS-derived navigation solutions.
The positioning signal will be generated by a Rb clock and an architecture similar to the GPS timekeeping system will be employed.