RS-422
RS-422, also known as TIA/EIA-422, is a technical standard originated by the Electronic Industries Alliance, first issued in 1975, that specifies electrical characteristics of a digital signaling circuit.
[1] RS-422 is the common short form title of American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standard ANSI/TIA/EIA-422-B Electrical Characteristics of Balanced Voltage Differential Interface Circuits and its international equivalent ITU-T Recommendation T-REC-V.11,[2] also known as X.27.
These technical standards specify the electrical characteristics of the balanced voltage digital interface circuit.
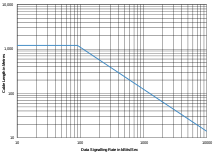
Figure A.1 shows a maximum length of 1,200 meters (3,900 ft), but this is with a termination, and the annex discusses the fact that many applications can tolerate greater timing and amplitude distortion, and that experience has shown that the cable length may be extended to several kilometers.
This figure is a conservative guide based on empirical data, not a limit imposed by the standard.
RS-422 cannot implement a true multi-point communications network, such as with RS-485, since there can be only one driver on each pair of wires.
While a double-pair cable may be practical for many RS-422 applications, the RS-422 specification only defines one signal path and does not assign any function to it.
These connectors are used to support RS-232 devices like modems, AppleTalk networking, RS-422 printers, and other peripherals.
This is the de facto industry standard connector for RS-422,[6] which is still found on broadcast equipment today.