Refractive index
The concept of refractive index applies across the full electromagnetic spectrum, from X-rays to radio waves.
Newton, who called it the "proportion of the sines of incidence and refraction", wrote it as a ratio of two numbers, like "529 to 396" (or "nearly 4 to 3"; for water).
[18] A type of new materials termed "topological insulators", was recently found which have high refractive index of up to 6 in the near to mid infrared frequency range.
[19] According to the theory of relativity, no information can travel faster than the speed of light in vacuum, but this does not mean that the refractive index cannot be less than 1.
[21] As an example, water has a refractive index of 0.99999974 = 1 − 2.6×10−7 for X-ray radiation at a photon energy of 30 keV (0.04 nm wavelength).
The resulting negative refraction (i.e., a reversal of Snell's law) offers the possibility of the superlens and other new phenomena to be actively developed by means of metamaterials.
[27] This is called dispersion and causes prisms and rainbows to divide white light into its constituent spectral colors.
Yellow spectral lines of helium (d) and sodium (D) are 1.73 nm apart, which can be considered negligible for typical refractometers, but can cause confusion and lead to errors if accuracy is critical.
All three typical principle refractive indices definitions can be found depending on application and region,[38] so a proper subscript should be used to avoid ambiguity.
That κ corresponds to absorption can be seen by inserting this refractive index into the expression for electric field of a plane electromagnetic wave traveling in the x-direction.
In special situations, especially in the gain medium of lasers, it is also possible that κ < 0, corresponding to an amplification of the light.
Forouhi and I. Bloomer deduced an equation describing κ as a function of photon energy, E, applicable to amorphous materials.
The refractive index and extinction coefficient, n and κ, are typically measured from quantities that depend on them, such as reflectance, R, or transmittance, T, or ellipsometric parameters, ψ and δ.
By fitting the theoretical model to the measured R or T, or ψ and δ using regression analysis, n and κ can be deduced.
For X-ray and extreme ultraviolet radiation the complex refractive index deviates only slightly from unity and usually has a real part smaller than 1.
According to Fermat's principle, light rays can be characterized as those curves that optimize the optical path length.
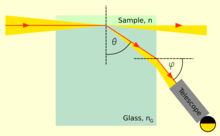
The numerical aperture in turn is determined by the refractive index n of the medium filling the space between the sample and the lens and the half collection angle of light θ according to Carlsson (2007):[46]: 6
In this technique the objective is dipped into a drop of high refractive index immersion oil on the sample under study.
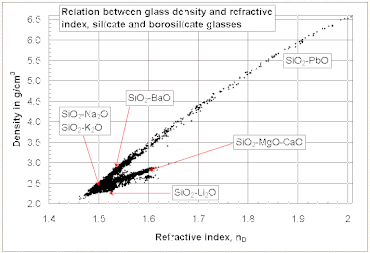
For liquids the same observation can be made as for gases, for instance, the refractive index in alkanes increases nearly perfectly linear with the density.
August Beer must have intuitively known that when he gave Hans H. Landolt in 1862 the tip to investigate the refractive index of compounds of homologeous series.
[52] While Landolt did not find this relationship, since, at this time dispersion theory was in its infancy, he had the idea of molar refractivity which can even be assigned to single atoms.
Empirical models can match experimental data over a wide range of materials and yet fail for important cases like InSb, PbS, and Ge.
[1]: 237 Light propagating in the direction of the optical axis will not be affected by the birefringence since the refractive index will be no independent of polarization.
In the more general case of trirefringent materials described by the field of crystal optics, the dielectric constant is a rank-2 tensor (a 3 by 3 matrix).
In this case the propagation of light cannot simply be described by refractive indices except for polarizations along principal axes.
[1]: 502 If the index varies quadratically with the field (linearly with the intensity), it is called the optical Kerr effect and causes phenomena such as self-focusing and self-phase modulation.
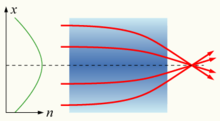
[1]: 273 Light traveling through such a medium can be bent or focused, and this effect can be exploited to produce lenses, some optical fibers, and other devices.
The phase cannot be measured directly at optical or higher frequencies, and therefore needs to be converted into intensity by interference with a reference beam.
After the specimen, the two parts are made to interfere, giving an image of the derivative of the optical path length in the direction of the difference in the transverse shift.
It can also be used as a useful tool to differentiate between different types of gemstone, due to the unique chatoyance each individual stone displays.