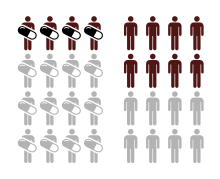
Relative risk reduction
In epidemiology, the relative risk reduction (RRR) or efficacy is the relative decrease in the risk of an adverse event in the exposed group compared to an unexposed group.
is the incidence in the exposed group, and
is the incidence in the unexposed group.
If the risk of an adverse event is increased by the exposure rather than decreased, the term relative risk increase (RRI) is used, and it is computed as
[1][2] If the direction of risk change is not assumed, the term relative effect is used, and it is computed in the same way as relative risk increase.