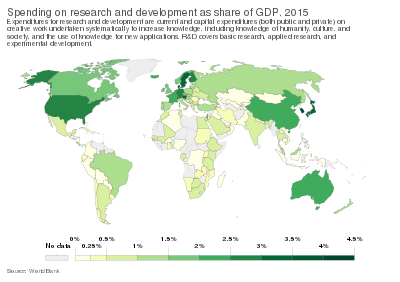
Research and development
[2][4] R&D differs from the vast majority of corporate activities in that it is not intended to yield immediate profit, and generally carries greater risk and an uncertain return on investment.
In a global industrial landscape that is changing fast, firms must continually revise their design and range of products.
[10] Statistics on organizations devoted to "R&D" may express the state of an industry, the degree of competition or the lure of progress.
In the United States, a typical ratio of research and development for an industrial company is about 3.5% of revenues; this measure is called "R&D intensity".
[citation needed] Research from 2000 has shown that firms with a persistent R&D strategy outperform those with an irregular or no R&D investment program.
[20] Therefore, firms may gain R&D profit that co-moves with takeover waves, causing risks to the company which engages in R&D activity.
[25] The federal research and development budget for fiscal year 2020 was $156 billion, 41.4% of which was for the Department of Defense (DOD).
In 1984, a law for Encouragement of Research and Development in Industry encouraged the commercial sector to invest in R&D in Israel as well as empowered the Office of Chief Scientist In the 1980s to 1992, the Chief scientist of Israel significantly expanded R&D subsidies in the Israeli industrial sector.
[31] Research and innovation in Europe are financially supported by the programme Horizon 2020, which is open to participation worldwide.
[32] A notable example is the European environmental research and innovation policy, based on the Europe 2020 strategy which will run from 2014 to 2020,[33] a multidisciplinary effort to provide safe, economically feasible, environmentally sound and socially acceptable solutions along the entire value chain of human activities.
[34] Firms that have embraced advanced digital technology devote a greater proportion of their investment efforts to R&D.
Firms who engaged in digitisation during the pandemic report spending a big portion of their expenditure in 2020 on software, data, IT infrastructure, and website operations.
[35][36] A 2021/2022 survey found that one in every seven enterprises in the Central, Eastern and South Eastern regions (14%) may be classed as active innovators — that is, firms that spent heavily in research and development and developed a new product, process, or service — however this figure is lower than the EU average of 18%.
[37] As of 2023, European enterprises account for 18% of the world's top 2 500 R&D corporations, but just 10% of new entrants, compared to 45% in the United States and 32% in China.
While 17% of the world’s top R&D investors are based in the European Union, they accounted for only 1% of acquisitions involving EU-based companies between 2013 and 2023.