Ring modulation
If one of the input signals has significant overtones (which is the case for square waves), the output will sound quite different, since each harmonic will generate its own pair of sidebands that won't be harmonically-related.
When the oscillators' frequencies are not harmonically related, ring modulation creates inharmonics, often producing bell-like or otherwise metallic sounds.
, whose Fourier expansion contains the fundamental and a series of reducing-amplitude odd harmonics: and the carrier frequency
[7] The original application was in the field of analog telephony for frequency-division multiplexing for carrying multiple voice signals over telephone cables.
It has since been applied to a wider range of uses, such as voice inversion, radio transceivers, and electronic music.
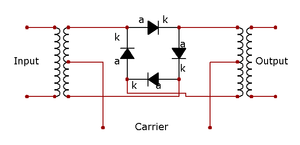
While the original Cowan patent describes a circuit with a ring of four diodes, later implementations used FETs as the switching elements.
The input and output stages typically include transformers with center-taps towards the diode ring.
Intermodulation products can be generated by carefully selecting and changing the frequency of the two input waveforms.
[8][failed verification] On an ARP Odyssey synthesizer (and a few others from that era as well) the ring modulator is an XOR function (formed from four NAND gates) fed from the square wave outputs of the two oscillators.
For the limited case of square or pulse wave signals, this is identical to true ring modulation.
In practical ring modulators, this leakage can be reduced by introducing opposing imbalances (e.g., variable resistors or capacitors).
[10][11] A ring modulator can be used to generate a double-sideband suppressed-carrier (DSB-SC) wave used in radio transmission.
[12] One of the earliest musical instruments utilizing a ring modulator was the Melochord (1947) built by Harald Bode.
[14] Meyer-Eppler mentioned the musical application of ring modulator in his book Elektrische Klangerzeugung, published in 1949.
[15] Meyer-Eppler's student Karlheinz Stockhausen used ring modulation in 1956 for some sounds in Gesang der Jünglinge and his realization score for Telemusik (1966[16]) also calls for it.
Indeed, several entire compositions by Stockhausen are based around it, such as Mixtur (1964), one of the first compositions for orchestra and live electronics; Mikrophonie II (1965), where the sounds of choral voices are modulated with a Hammond organ; Mantra (1970),[16] where the sounds from two pianos are routed through ring modulators; and Licht-Bilder (2002) from Sonntag aus Licht (2003),[1] which ring-modulates flute and trumpet.
[17][18][19] Other Stockhausen pieces employing ring modulation include Kontakte (1960),[1] Mikrophonie I (1964),[1] Hymnen (1969),[1] Prozession (1967),[1] and Kurzwellen (1968).
[1] A ring-modulator was the major component used in Louis and Bebe Barron's music for the film Forbidden Planet (1956).
One of the best-known applications of the ring modulator may be its use by Brian Hodgson of the BBC Radiophonic Workshop to produce the distinctive voice of the Daleks in the television series Doctor Who, starting in 1963.
Also in 1964 he developed the Bode Frequency Shifter, which produced a clearer sound by eliminating a side band.
[23] In 1963, Don Buchla included an optional ring modulator in his first modular synthesizer, the Model 100.
The EMS VCS3, Synthi A, ARP 2600, Odyssey, Rhodes Chroma and Yamaha CS-80 synthesizers also featured built-in ring modulators.
John McLaughlin employs the ring modulator heavily in the 1974 Mahavishnu Orchestra album Visions of the Emerald Beyond, especially on the track "On the Way Home to Earth".
On Miles Davis' 1975 live album Agharta, guitarist Pete Cosey ran the sounds he played through a ring modulator.
[29] Deep Purple's Jon Lord fed the signal from his Hammond through a Gibson Ring Modulator unit live on stage, which he described in 1989.
[30][31] Founding member of Hawkwind, Dik Mik, a self-confessed non-musician, used a ring modulator as his main instrument during his time with the band (1969-1973).
The music on the album is often atonal, with the ring modulator converting the synthesizer's sound into complex metallic timbres.
[33] It remains the most experimental released work by the artist, with reviewers calling it "difficult listening at best".
A ring modulator in combination with carrier wave and filter was used to assign channels to different frequencies.
Early attempts at securing analog telephone channels used ring modulators to modify the spectrum of the audio speech signals.