Road
[6] Part 2, Division 1, clauses 11–13 of the National Transport Commission Regulations 2006 defines a road in Australia as 'an area that is open to or used by the public and is developed for, or has as one of its main uses, the driving or riding of motor vehicles.
[9] Beaches, publicly accessible car parks and yards (even if privately owned), river beds, road shoulders (verges), wharves and bridges are included.
[12] This includes footpaths, bridleways and cycle tracks, and also road and driveways on private land and many car parks.
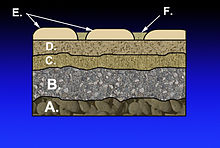
In transport engineering, subgrade is the native material underneath a constructed road.Road construction requires the creation of an engineered continuous right-of-way or roadbed, overcoming geographic obstacles and having grades low enough to permit vehicle or foot travel,[42]: 15 and may be required to meet standards set by law[43] or official guidelines.
[37] The radii and gradient are designed and staked out to best suit the natural ground levels and minimize the amount of cut and fill.
[44]: 34 Great care is taken to preserve reference Benchmarks[44]: 59 Roads are designed and built for primary use by vehicular and pedestrian traffic.
Drainage lines are laid with sealed joints in the road easement with runoff coefficients and characteristics adequate for the land zoning and storm water system.
Approval from local authorities may be required to draw water or for working (crushing and screening) of materials for construction needs.
Blasting is not frequently used to excavate the roadbed as the intact rock structure forms an ideal road base.
[44]: 68–69 General fill material should be free of organics, meet minimum California bearing ratio (CBR) results and have a low plasticity index.
The lower fill generally comprises sand or a sand-rich mixture with fine gravel, which acts as an inhibitor to the growth of plants or other vegetable matter.
Safety improvements such as traffic signs, crash barriers, raised pavement markers and other forms of road surface marking are installed.
Drivers living in urban areas with populations more than 250,000 are paying upwards of $750 more annually because of accelerated vehicle deterioration, increased maintenance, additional fuel consumption, and tire wear caused by poor road conditions.
[59] Some roads like Chicago's Wacker Drive, a major two-level (and at one point, three-level) roadway in the downtown area, are being rebuilt with a designed service life of 100 years.
Thin surfacing preserves, protects and improves the functional condition of the road while reducing the need for routing maintenance, leading to extended service life without increasing structural capacity.
A 2009 report released by the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials estimated that about 50% of the roads in the US are in bad condition, with urban areas worse.
The three steps for this method after finding the voids are locating and drilling holes, grout injection and post-testing the stabilized slabs.
Slab stabilization does not correct depressions, increase the design structural capacity, stop erosion or eliminate faulting.
It is recommended to do this testing at night as during cooler temperatures, joints open, aggregate interlock diminishes and load deflections are at their highest.
Ground penetrating radar pulses electromagnetic waves into the pavement and measures and graphically displays the reflected signal.
The injection device must also have a return hose or a fast-control reverse switch, in case workers detect slab movement on the uplift gauge.
There are various materials to choose for this method including hot pour bituminous liquid, silicone and preformed compression seals.
Botts dots are not used where it is icy in the winter, because frost and snowplows can break the glue that holds them to the road, although they can be embedded in short, shallow trenches carved in the roadway, as is done in the mountainous regions of California.
Road runoff is a major source of nickel, copper, zinc, cadmium, lead and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), which are created as combustion byproducts of gasoline and other fossil fuels.
[75] De-icing chemicals and sand can run off into roadsides, contaminate groundwater and pollute surface waters;[76] and road salts can be toxic to sensitive plants and animals.
[80] In addition, on-road transportation greenhouse gas emissions are the largest single cause of climate change, scientists say.
Bahrain is the only island country to be connected to a continental network by road (the King Fahd Causeway to Saudi Arabia).
Even on mainlands, some settlements have no roads connecting with the primary continental network, due to natural obstacles like mountains or wetlands, or high cost compared to the population served.
Where demand for travel by road vehicle to a disconnected island or mainland settlement is high, roll-on/roll-off ferries are commonly available if the journey is relatively short.
For example, resupply aircraft are only flown to Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station October to February, and many residents of coastal Alaska have bulk cargo shipped in only during the warmer months.