Satellite internet constellation
[2] As of 2020, 63 percent of rural households worldwide lacked internet access due to the infrastructure requirements of underground cables and network towers.
[17] All three companies had formerly focused on the provision of communication services from GEO and MEO orbits, while the newer satellite internet providers have been fielding their constellations exclusively in LEO.
[17] In 2018, the Russian government established the Sfera (Sphere) constellation program, to consist of 162 satellites, providing broadband internet connectivity, message relay, video broadcast, and remote sensing services.
[18] Proposed systems vary greatly in the number of satellites, the types of orbits and the telecommunication architecture (in particular the presence or absence of inter-satellite links).
[20] For continental distances (greater than about 3,000 km[21]), LEO satellite internet networks are expected to be able to provide lower latency than optical fiber links.
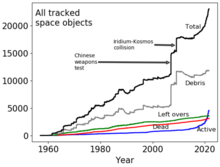
[31] Additional research is needed to determine impact of (inter alia) light pollution on various locations, communities, indigenous peoples, and other forms of observation.
A report from the SATCON1 workshop in 2020 concluded that the effects of large satellite constellations can severely affect some astronomical research efforts and lists six ways to mitigate harm to astronomy.
[32][33] In 2022, the IAU announced the Centre for the Protection of the Dark and Quiet Sky from Satellite Constellation Interference to coordinate or aggregate measures to mitigate such detrimental effects.