Scanning vibrating electrode technique
It was originally introduced in 1974 by Jaffe and Nuccitelli to investigate the electrical current densities near living cells.
[2] SVET measures local current density distributions in the solution above the sample of interest, to map electrochemical processes in situ as they occur.
[4] Scanning vibrating electrode technique was originally introduced to sensitively measure extracellular currents by Jaffe and Nuccitelli in 1974.
Using SRET it is possible to determine the anodic and cathodic sites of a corroding sample without the probe altering the corrosion process.
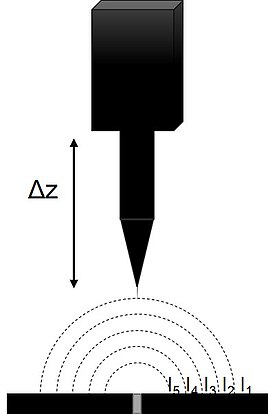
In SVET, the probe vibration results in a more sensitive measurement than its non-vibrating predecessors,[1] as well as giving rise to an improvement of the signal-to-noise ratio.
When all other variables are equal a smaller probe to sample distance will result in the measurement of a higher magnitude signal.
[20] Through the use of SVET it has been possible to investigate the effect of changing the aluminum spacer width on the galvanic coupling between steel and magnesium, a pairing which can be found on automobiles.
[22][23][24] A number of groups have used SVET to analyze the efficiency of self-healing coatings, mapping the changes in surface activity over time.
al. have performed a number of studies on SAMs formed on different metals to investigate their corrosion inhibition using SVET.
[32] Using vibrating probe, the electrical currents involved in the biological processes occurring at leaves have been measured.
[38] SVET has been used to investigate the photoconductive nature of semiconductor materials, by following changes in current density related to photoelectrochemical reactions.