Schierstein Bridge
Crossing two arms of the Rhine and the intervening island of Rettbergsaue, the bridge is made of six individual structures, including 100 m (330 ft) from prestressed concrete.
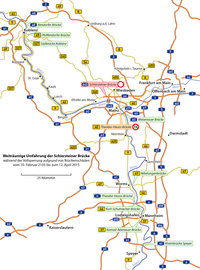
From mid-February to mid-April 2015 the bridge was closed from all traffic due to extensive structural damage.
At the end of the 1950s and early 1960s, the states of Hesse and Rhineland-Palatinate began an extensive road construction program to further the development of the Rhine-Main Region.
The production of sub-units of the superstructure and their assembly into larger units were made in large part in the workshop.
The entire steel structure was delivered to the site by water from Düsseldorf on a rented boat and installed.
This required an elevated bridge structure (the Hochstraße Lenneberg), with 31 piers, spanning the Mombach floodplain.
Several street lights were installed to illuminate the junction, but, for cost reasons, these remain dark today.
Today, the design capacity is regularly exceeded by a factor of 3, which in turn led to extensive damage to the reinforced concrete structure.
Two spiral staircases allow access for pedestrians and cyclists on the left and right side of the bridge, directly over the summer dam of the Rhine.
The abutments and land supports were built as single columns with a circular cross-section and founded on footings.
[1] Since most of the Schiersteiner Bridge is in Hesse, and the smaller part in Rhineland-Palatinate, it was decided through arrangements between the two states that the Hessian administration would alone be responsible for its maintenance.
This is also confirmed by the respective names of the bridges: Schierstein is a borough of Wiesbaden and Weisenau part of Mainz.
Over the years, the bridge has had to handle an ever-increasing traffic load, but, with the exception of re-painting, conservation measures were not carried out.
Surface cracks and damaged areas of the deck sealing also allowed localized high chloride stress in the concrete.
Although the viability and stability of the bridge were only partially affected, urgent repairs were needed to ensure its continued usability and durability.