Scrum (software development)
Scrum is an agile team collaboration framework commonly used in software development and other industries.
Scrum prescribes for teams to break work into goals to be completed within time-boxed iterations, called sprints.
[2] Scrum's approach to product development involves bringing decision-making authority to an operational level.
Based on case studies from manufacturing firms in the automotive, photocopier, and printer industries, the authors outlined a new approach to product development for increased speed and flexibility.
[8] Sutherland and Schwaber later worked together to integrate their ideas into a single framework, formally known as scrum.
Schwaber and Sutherland tested scrum and continually improved it, leading to the publication of a research paper in 1995,[9] and the Manifesto for Agile Software Development in 2001.
[10] Schwaber also collaborated with Babatunde Ogunnaike at DuPont Research Station and the University of Delaware to develop Scrum.
Ogunnaike believed that software development projects could often fail when initial conditions change if product management was not rooted in empirical practice.
[12] Since 2009, a public document called The Scrum Guide[13] has been published and updated by Schwaber and Sutherland.
The product owner liaises with stakeholders, those who have an interest in the project's outcome, to communicate tasks and expectations with developers.
The role is intended to primarily represent the product's stakeholders, the voice of the customer, or the desires of a committee, and bears responsibility for the delivery of business results.
[21][22] As the primary liaison of the scrum team towards stakeholders, product owners are responsible for communicating announcements, project definitions and progress, RIDAs (risks, impediments, dependencies, and assumptions), funding and scheduling changes, the product backlog, and project governance, among other responsibilities.
[1] Scrum masters have differing roles and responsibilities from traditional team leads or project managers.
Some scrum master responsibilities include coaching, objective setting, problem solving, oversight, planning, backlog management, and communication facilitation.
[31] It can be done as a separate stage done before the beginning of a new sprint or as a continuous process that team members work on by themselves.
Backlog refinement can include the breaking down of large tasks into smaller and clearer ones, the clarification of success criteria, and the revision of changing priorities and returns.
Artifacts are a means by which scrum teams manage product development by documenting work done towards the project.
Team members self organize by pulling work as needed according to the backlog priority and their own capabilities and capacity.
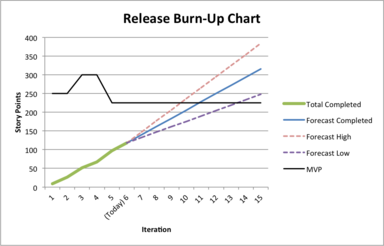
Updated at the end of each sprint, the release burn-up chart shows progress towards delivering a forecast scope.
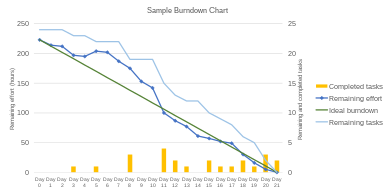
The collection of historical "velocity" data is a guideline for assisting the team in understanding their capacity.