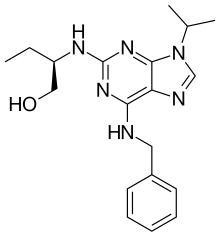
Seliciclib
Seliciclib has previously undergone Phase IIa clinical trials, in 240 NSCLC patients as a combined dose with existing first- and second-line treatments.
[9] If this mechanism turns out to be safe, reliable and efficient in vivo, the drug could improve treatment of chronic inflammation diseases such as cystic fibrosis and arthritis.
These are usually treated with glucocorticoids which often have serious side effects In the nervous system, seliciclib has been shown to suppress microglial activation[10] and to provide some neuroprotection in animal models of cerebral ischemia.
[11][12] Furthermore, it increases antitumor activity of temozolomide in treatment of glioblastoma multiforme and is considered as a possible therapeutic option for glioma.
Seciclib causes egg activation by inhibiting protein kinases which results in the inactivation of the maturation promoting factor (MPF).