Semigallia
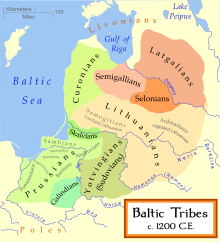
Semigallia[a] is one of the Historical Latvian Lands located to the south of the Daugava and to the north of the Saule region of Samogitia.
They occupied a smaller area of the coast on the Gulf of Riga in the north and didn't reach the Daugava in the northeast.
[4] The neighbouring tribes were the Livonians in the north, the Latgalians in the northeast, the Selonians in the east, the Aukštaitians in the south, the Samogitians in the southwest, and the Curonians in the west.
Six Semigallian lands were known in the first half of the 13th century: Dobene, Dobele, Silene, Spārnene, Tērvete, Upmale, Žagare.
The Mervala stone in Sweden contains runic inscriptions which read: Which, in English, translates as: In the first half of the 13th century, settlements along the Daugava river were quite often attacked by the Lithuanians.
The Livonian Order, which had begun conquering eastern Semigallia around the same period, made an alliance with the Semigallians and the Latgalians against the Lithuanians.
In the winter of 1205, an army of Semigallians led by Viestards attacked the forces of Lithuanian Duke Žvelgaitis, who was returning from a war against Estonia with booty and Estonian slaves.
1,200 Lithuanian knights perished; the Estonian slaves were slaughtered as well, in retribution for "past crimes" against the Livonians.
Lithuanians passed through Semigallia to raid settlements in Livonia, and they took advantage of the winter ice pack in the Gulf of Riga to reach Oesel Island.
In 1279, after the victory of the Lithuanians in the battle of Aizkraukle, the final Semigallian uprising started, led by Duke Nameisis.
In 1281, Nameisis, along with many of his compatriots, withdrew to Lithuania and, in the same year, took part in battles led by Traidenis against the Teutonic Order.
On the coat of arms of Latvia, Semigallia is represented along with Courland (Kurzeme), due to the historical connection between the two regions.
Semigallia borders other historical Baltic regions such as Vidzeme (the southern part of former Swedish Livonia) to the northeast, Lithuanian Samogitia to the south, Courland to the west and Selonia to the east as well as the Gulf of Riga to the north.
The major town is Jelgava (German: Mitau), the former capital of the united Duchy of Courland and Semigallia.
Žiemgala is part of Aukštaitija; its main centres are Joniškis, Pakruojis, Žeimelis, Linkuva and Pasvalys.