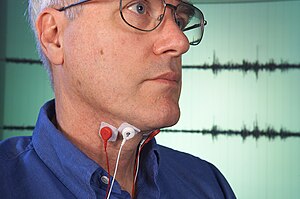
Subvocal recognition
[2] Silent speech interface systems have been created using ultrasound and optical camera input of tongue and lip movements.
[5][6] Another source of information is the vocal tract resonance signals that get transmitted through bone conduction called non-audible murmurs.
[3][10] In 2002, the Japanese company NTT DoCoMo announced it had created a silent mobile phone using electromyography and imaging of lip movement.
The company stated that "the spur to developing such a phone was ridding public places of noise," adding that, "the technology is also expected to help people who have permanently lost their voice.
[13] With a grant from the U.S. Army, research into synthetic telepathy using subvocalization is taking place at the University of California, Irvine under lead scientist Mike D'Zmura.