Smart charging
[3] For UMC, a Time-of-Use tariff is applied, and the customer decides the timing to charge based on the price and needs.
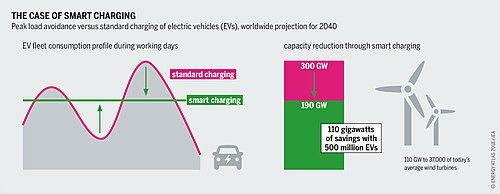
Ideally, the EV charging peak is self-adjustable to fit the real-time electricity demand gap at off-peak hours.
In UMC systems, electricity pricing with respect to time is a simple form of incentive.
V2G is a smart charging implementation where the utility/transmission system is capable of purchasing energy from customers, usually during peak hours.
Discharging provides extra flexibility to the grid by extending the power range and may shave the peak in electricity production.
[3] Perceptions among Actual and Potential Plug-in Electric Vehicle Adopters in the United Kingdom) Some of the general concerns are addressed below.
Studies have shown that car sharing will lead to a reduction in private vehicle use with a low occupancy rate.
This means chargepoints must be able to be remotely accessed, and capable of receiving, interpreting and reacting to a signal.
Charging stations locations, cost and the ability to respond to demand shift (i.e. the charging/ discharging power) are the limiting factors.