Space research
In Russia, Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, in the United States, Robert H. Goddard, and in Germany, Hermann Oberth.
The space research field evolved as scientific investigation based on advancing rocket technology.
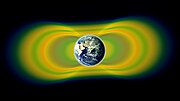
As higher altitudes were reached, space physics emerged as a field of research with studies of Earths aurorae, ionosphere and magnetosphere.
The major discovery of satellite research was in 1958, when Explorer 1 detected the Van Allen radiation belts.
Planetology reached a new stage with the Russian Luna programme, between 1959 and 1976, a series of lunar probes which gave us evidence of the Moons chemical composition, gravity, temperature, soil samples, the first photographs of the far side of the Moon by Luna 3, and the first remotely controlled robots (Lunokhod) to land on another planetary body.
On April 19, 1971, the Soviet Union launched the Salyut 1, the first space station of substantial duration, a successful 23 day mission, sadly ruined by transport disasters.
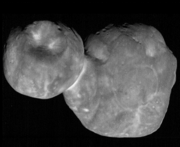
Originally designated "1110113Y" when detected by Hubble in 2014, the planetessimal was reached by the New Horizons probe on 1 January 2019 after a week long manoeuvering phase.
The Voyager 1 probe launched on 5 September 1977, and flew beyond the edge of our solar system in August 2012 to the interstellar medium.
The farthest human object from the Earth, predictions include collision, an Oort cloud, and destiny, "perhaps eternally—to wander the Milky Way."
The Great Observatories program pushes forward our understanding of the universe with detailed observation of the sky, based in gamma rays, ultraviolet, x-ray, infrared, and visible, light spectrums.
In the present day, the Hubble is used to identify exo-planets and give detailed accounts of events in our own solar system.
Hubbles visible-light observations are combined with the other great observatories to give us some of the most detailed images of the visible universe.
INTEGRAL is one of the most powerful gamma-ray observatories, launched by the European Space Agency in 2002, and continuing to operate (as of March 2019).
INTEGRAL provides insight into the most energetic cosmological formations in space including, black holes, neutron stars, and supernovas.
Occupied in low Earth orbit for twelve and a half years, Mir served a permanent microgravity laboratory.