Strain wave gearing
Disadvantages include a tendency for 'wind-up' (a torsional spring rate) in the low torque region.
Musser in a 1957 patent[5][6] while he was an advisor at United Shoe Machinery Corp (USM).
[7][8]In 1971, on NASA's Apollo 15 mission, the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was driven by one electric motor per wheel - connected by 80:1 Harmonic Drive gears.
More complex versions have a fourth component normally used to shorten the overall length or to increase the gear reduction within a smaller diameter, but still follow the same basic principles.
The flex spline fits tightly over the wave generator, so that when the wave generator plug is rotated, the flex spline deforms to the shape of a rotating ellipse and does not slip over the outer elliptical ring of the ball bearing.
The ball bearing lets the flex spline rotate independently to the wave generator's shaft.
The electrically driven wheels of the Apollo Lunar Rover included strain wave gears.
[11] Also, the winches used on Skylab to deploy the solar panels were powered using strain wave gears.
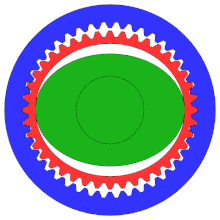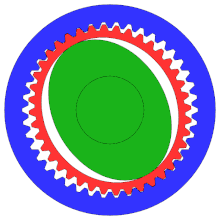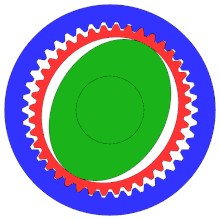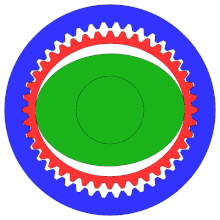
- Outer circle: circular spline (fixed)
- Middle circle: flex spline (attached to output shaft, not shown)
- Inner oval: wave generator (attached to input shaft; inner ball bearing and shaft, not shown)


- input shaft
- wave generator
- flexspline
- circular spline
- output shaft
- housing