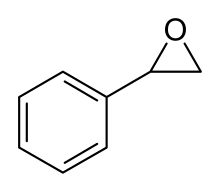
Styrene oxide
A trace amount of acid in water causes hydrolysis to racemic phenylethyleneglycol via a benzylic cation.
If the amount of water is not sufficient, acid-catalyzed isomerization for phenylacetaldehyde will occur.
It is considered possibly carcinogenic from gavaging significant amounts into mice and rats.
It was also found that (S)-styrene oxide was preferentially hydrolyzed than the R enantiomer in human liver microsomes.
Animal studies have shown that the (R)-enantiomer of styrene oxide was more toxic than the (S)-enantiomer in mice.