Suspended load
The suspended load of a flow of fluid, such as a river, is the portion of its sediment uplifted by the fluid's flow in the process of sediment transportation.
The suspended load generally consists of smaller particles, like clay, silt, and fine sands.
The suspended load is one of the three layers of the fluvial sediment transportation system.
The bed load consists of the larger sediment which is transported by saltation, rolling, and dragging on the riverbed.
The boundary between bed load and suspended load is not straightforward because whether a particle is in suspension or not depends on the flow velocity – it is easy to imagine a particle moving between bed load, part-suspension and full suspension in a fluid with variable flow.
Suspended load generally consists of fine sand, silt and clay size particles although larger particles (coarser sands) may be carried in the lower water column in more intense flows.
Suspended loads required the Velocity to keep the sediment transporting above the bed.
The suspended load is carried within the lower to middle part of the water column and moves at a large fraction of the mean flow velocity of the stream, with a Rouse number between 0.8 and 1.2.
The rates within the Rouse number reveal how at which the sediment will transport at the current velocity.
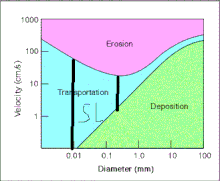
The Hjulström curve uses velocity and sediment size to compare the rate of erosion, transportation, and deposition.
While the diagram shows the rate, one flaw about the Hjulström Diagram is that it doesn't show the depth of the creek giving an estimated rate.
The Shields Diagram is considered a more precise chart to estimate suspended load.
[1][2] To find the stream power for sediment transportation, shear stress helps determine the force required to allow sediment transportation.