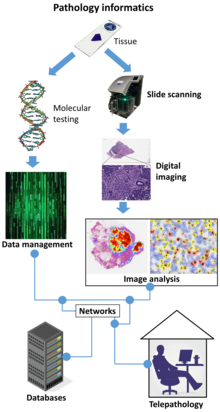
Telepathology
It uses telecommunications technology to facilitate the transfer of image-rich pathology data between distant locations for the purposes of diagnosis, education, and research.
[3] The use of "television microscopy", the forerunner of telepathology, did not require that a pathologist have physical or virtual "hands-on" involvement in the selection of microscopic fields-of-view for analysis and diagnosis.
In a medical journal editorial, Weinstein outlined the actions that would be needed to create remote pathology diagnostic services.
A number of clinical telepathology services have benefited many thousands of patients in North America, Europe, and Asia.
With real-time systems, the consultant actively operates a robotically controlled motorized microscope located at a distant site—changing focus, illumination, magnification, and field of view—at will.
While real-time and virtual slide systems offer higher diagnostic accuracy when compared with static-image telepathology, there are drawbacks to each.
Storing and simultaneously retrieving large numbers of telepathology whole-slide image files can be cumbersome, introducing their own workflow challenges in the clinical laboratory.
Canada Health Infoway has targeted funding of $1.2 million CAD to the Telepathology Solution for the province of British Columbia.