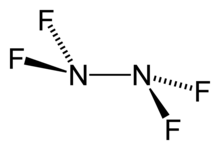
Tetrafluorohydrazine
[2] It adds across double bonds to give vicinal di(difluoroamine)s.[8] In chemical syntheses, as a precursor or a catalyst.
[2] Tetrafluorohydrazine explodes or ignites on contact with reducing agents at room temperature, including hydrogen, hydrocarbons, alcohols, thiols, amines, ammonia, hydrazines, dicyanogen, nitroalkanes, alkylberylliums, silanes, boranes or powdered metals.
Prolonged exposure of the container of tetrafluorohydrazine to high heat may cause it to rupture violently and rocket.
When heated to decomposition in air, it emits highly toxic fumes of fluorine and oxides of nitrogen.
[2] There is a fatal case in which during opening of valves to check the pressure, the cylinder exploded, killing one man and injuring another.