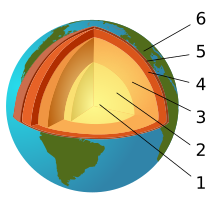
Natural environment
This environment encompasses the interaction of all living species, climate, weather and natural resources that affect human survival and economic activity.
Even acts which seem less extreme, such as building a mud hut or a photovoltaic system in the desert, the modified environment becomes an artificial one.
Though many animals build things to provide a better environment for themselves, they are not human, hence beaver dams and the works of mound-building termites are thought of as natural.
Earth science generally recognizes four spheres, the lithosphere, the hydrosphere, the atmosphere and the biosphere[3] as correspondent to rocks, water, air and life respectively.
These major disciplines use physics, chemistry, biology, chronology and mathematics to build a qualitative and quantitative understanding of the principal areas or spheres of Earth.
The Earth's crust or lithosphere, is the outermost solid surface of the planet and is chemically, physically and mechanically different from underlying mantle.
It has been generated greatly by igneous processes in which magma cools and solidifies to form solid rock.
Humans impact the water in different ways such as modifying rivers (through dams and stream channelization), urbanization and deforestation.
The changing vegetation occurs because when trees cannot get adequate water they start to deteriorate, leading to a decreased food supply for the wildlife in an area.
Many natural substances may be present in tiny amounts in an unfiltered air sample, including dust, pollen and spores, sea spray, volcanic ash and meteoroids.
The ozone layer of the Earth's atmosphere plays an important role in reducing the amount of ultraviolet (UV) radiation that reaches the surface.
[17] These scientists are increasingly concerned about the potential long-term effects of global warming on our natural environment and on the planet.
Of particular concern is how climate change and global warming caused by anthropogenic, or human-made releases of greenhouse gases, most notably carbon dioxide, can act interactively and have adverse effects upon the planet, its natural environment and humans' existence.
[18] This warming is also responsible for the extinction of natural habitats, which in turn leads to a reduction in wildlife population.
[19] Efforts have been increasingly focused on the mitigation of greenhouse gases that are causing climatic changes, on developing adaptative strategies to global warming, to assist humans, other animal, and plant species, ecosystems, regions and nations in adjusting to the effects of global warming.
Weather refers, generally, to day-to-day temperature and precipitation activity, whereas climate is the term for the average atmospheric conditions over longer periods of time.
Weather systems in the mid-latitudes, such as extratropical cyclones, are caused by instabilities of the jet stream flow.
Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the atmosphere for a future time and a given location.
Living organisms undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, possess a capacity to grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce and, through natural selection, adapt to their environment in successive generations.
[34] Central to the ecosystem concept is the idea that living organisms are continually engaged in a highly interrelated set of relationships with every other element constituting the environment in which they exist.
Eugene Odum, one of the founders of the science of ecology, stated: "Any unit that includes all of the organisms (i.e.: the "community") in a given area interacting with the physical environment so that a flow of energy leads to clearly defined trophic structure, biotic diversity, and material cycles (i.e.: exchange of materials between living and nonliving parts) within the system is an ecosystem.
"[35] The human ecosystem concept is then grounded in the deconstruction of the human/nature dichotomy, and the emergent premise that all species are ecologically integrated with each other, as well as with the abiotic constituents of their biotope.
This is not universally the case and there is no proven relationship between the species diversity of an ecosystem and its ability to provide goods and services on a sustainable level.
Global biogeochemical cycles are critical to life, most notably those of water, oxygen, carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus.
[36] Wilderness is generally defined as a natural environment on Earth that has not been significantly modified by human activity.
"[37] Wilderness areas and protected parks are considered important for the survival of certain species, ecological studies, conservation, solitude, and recreation.
This way of looking at wilderness includes areas within which natural processes operate without very noticeable human interference.
Domesticating wild plant and animal species for human benefit has occurred many times all over the planet, and has a major impact on the environment, both positive and negative.
While true wilderness is increasingly rare, wild nature (e.g., unmanaged forests, uncultivated grasslands, wildlife, wildflowers) can be found in many locations previously inhabited by humans.
[48] Specifically in the United States and Arabian countries many native cultures do not recognize the "environment", or see themselves as environmentalists.