Timber framing
The decorative manner of half-timbering is promoted in Germany by the German Timber-Frame Road, several planned routes people can drive to see notable examples of Fachwerk buildings.
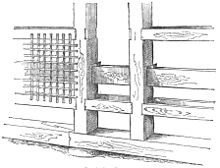
This juxtaposition of exposed timbered beams and infilled spaces created the distinctive "half-timbered", or occasionally termed, "Tudor" style, or "black-and-white".
Wood hangars were constructed throughout North America and employed various technologies including bowstring, Warren, and Pratt trusses, glued laminated arches, and lamella roof systems.
Shear plate connectors resembled large washers, deformed on the side facing the timber in order to grip it, and were through-fastened with long bolts or lengths of threaded rod.
[20] SIPs reduce dependency on bracing and auxiliary members, because the panels span considerable distances and add rigidity to the basic timber frame.
Some firms have specialized in industrial prefabrication of such residential and light commercial structures such as Huf Haus as low-energy houses or – dependent on location – zero-energy buildings.
Such buildings must be designed to accommodate the poor thermal insulating properties of mudbrick, however, and usually have deep eaves or a veranda on four sides for weather protection.
Timber framing is rare in Russia, Finland, northern Sweden, and Norway, where tall and straight lumber, such as pine and spruce, is readily available and log houses were favored, instead.
Europe is full of timber-framed structures dating back hundreds of years, including manors, castles, homes, and inns, whose architecture and techniques of construction have evolved over the centuries.
Some of the earliest known timber houses in Europe have been found in Great Britain, dating to Neolithic times; Balbridie and Fengate are some of the rare examples of these constructions.
Half-timbered construction traveled with British colonists to North America in the early 17th century but was soon abandoned in New England and the mid-Atlantic colonies for clapboard facings (an East Anglia tradition).
The original English colonial settlements, such as Plymouth, Massachusetts and Jamestown, Virginia had timber-framed buildings, rather than the log cabins often associated with the American frontier.
[42] Elaborately half-timbered houses of the 13th through 18th centuries still remain in Bourges, Tours, Troyes, Rouen, Thiers, Dinan, Rennes, and many other cities, except in Provence and Corsica.
The German fachwerkhaus usually has a foundation of stone, or sometimes brick, perhaps up to several feet (a couple of metres) high, which the timber framework is mortised into or, more rarely, supports an irregular wooden sill.
[45][46] In addition there is a myriad of regional scrollwork and fretwork designs of the non-loadbearing large timbers (braces) peculiar to particularly wealthy towns or cities.
Although the typical Basque house is now mostly associated with half-timbering, the outer walls and the fire-walls were built in masonry (rubble stone, bricks or, ideally, ashlars) whenever it could be afforded.
Extant baserriak with half-timbered upper-floor façades were built from the 15th to 19th centuries and are found in all Basque regions with oceanic climate, except in Zuberoa (Soule), but are concentrated in Lapurdi (Labourd).
Grindverk translates as trestle construction, consisting of a series of transversal frames of two posts and a connecting beam, supporting two parallel wall plates bearing the rafters.
Archaeological excavations have uncovered similar wooden joints from more than 3,000 years ago, suggesting that this type of framing is an ancient unbroken tradition.
Timber framing of the type used in large parts of Europe appeared occasionally in late medieval towns, but never became common, except for the capital Christiania.
He outlawed log building to prevent future conflagrations and required wealthy burghers to use brickwork and the less affluent to use timber framing in the Danish manner.
It was in North Holland where the import of cheaper timber, combined with the Dutch innovation of windmill-powered sawmills, allowed economically viable widespread use of protective wood covering over framework.
[50] Half-timbered houses can be found in Romania mostly in areas once inhabited by Transylvanian Saxons, in cities, towns and villages with Germanic influence such as Bistrița, Brașov, Mediaș, Sibiu and Sighișoara.
Piece-sur-piece, also known as Post-and-plank style or "corner post construction" (and many other names) in which wood is used both for the frame and horizontal infill; for this reason it may be incorrect to call it "half-timbering".
This technique of a timber frame walls filled in with horizontal planks or logs proved better suited to the harsh climates of Québec and Acadia, which at the same time had abundant wood.
In the revival styles, such as Tudorbethan (Mock Tudor), the half-timbered appearance is superimposed on the brickwork or other material as an outside decorative façade rather than forming the main frame that supports the structure.
Such houses are notoriously expensive to maintain let alone renovate and restore, most commonly owing to local regulations that do not allow divergence from the original, modification or incorporation of modern materials.
One major problem with older structures is the phenomenon known as mechano-sorptive creep or slanting: where wood beams absorb moisture whilst under compression or tension strains and deform, shift position or both.
This is a major structural issue as the house may deviate several degrees from perpendicular to its foundations (in the x-axis, y-axis, and even z-axis) and thus be unsafe and unstable or so out of square it is extremely costly to remedy.
[59] A summary of problems with Fachwerkhäuser or half-timbered houses includes the following, though many can be avoided by thoughtful design and application of suitable paints and surface treatments and routine maintenance.