Time in Africa
[10] Other countries followed suit, and by 1912, most Portuguese,[11] French and British territories had adopted a standard offset.
[12] Liberia was the last country in Africa to adopt a standard offset, doing so on 7 January 1972.
This would soon be followed by Egypt, which adopted standard time on 1 October 1900;[21][22] Nigeria adopted standard time on 1 July 1905,[23] Seychelles in 1906,[24] Mauritius on 1 January 1907,[21] Togo in 1907,[12] Algeria on 11 March 1911[9] and Tunisia on 12 April 1911.
[13] The latest time change was South Sudan, which switched from UTC+3 to +2 on 1 February 2021.
[27] As Africa straddles the equator and tropics, there is little change in daylight hours throughout the year[4] and as such daylight saving time (DST) is currently observed in only one country, Morocco, however it was also previously observed in several other countries: the countries that formerly observed DST are South Africa, which last observed it in 1944,[28] Cape Verde in 1945,[29] Madagascar in 1954,[29] Ghana in 1956,[30] Sierra Leone in 1962,[31] Algeria and Chad in 1980,[9] Sudan in 1985,[9] Tunisia in 2008,[32] Mauritius in 2009,[29] Libya in 2012,[33][34] Egypt in 2015,[35] and Namibia in 2017.
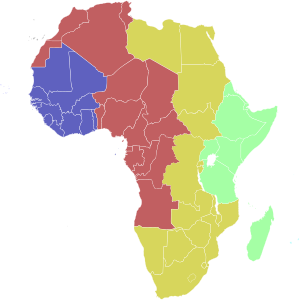
| Light Blue | Cape Verde Time [a] ( UTC−1 ) |
| Blue | Greenwich Mean Time ( UTC ) |
| Red | ( UTC+1 ) |
| Ochre | ( UTC+2 ) |
| Green | East Africa Time ( UTC+3 ) |
| Turquoise | ( UTC+4 ) |
b Mauritius and the Seychelles are to the east and north-east of Madagascar respectively.