Time in physics
Time can be combined mathematically with other physical quantities to derive other concepts such as motion, kinetic energy and time-dependent fields.
It has been defined since 1967 as "the duration of 9192631770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the caesium 133 atom", and is an SI base unit.
The relative accuracy of such a time standard is currently on the order of 10−15[13] (corresponding to 1 second in approximately 30 million years).
The caesium atomic clock became practical after 1950, when advances in electronics enabled reliable measurement of the microwave frequencies it generates.
According to the prevailing cosmological model of the Big Bang theory, time itself began as part of the entire Universe about 13.8 billion years ago.
The regular recurrences of the seasons, the motions of the sun, moon and stars were noted and tabulated for millennia, before the laws of physics were formulated.
[15] In particular, the astronomical observatories maintained for religious purposes became accurate enough to ascertain the regular motions of the stars, and even some of the planets.
Richard of Wallingford (1292–1336), abbot of St. Albans Abbey, famously built a mechanical clock as an astronomical orrery about 1330.
In this section, the relationships listed below treat time as a parameter which serves as an index to the behavior of the physical system under consideration.
Calendars and ship's logs could then be mapped to the march of the hours, days, months, years and centuries.
Rudolf Clausius (1822–1888) noted a measure of disorder, or entropy, which affects the continually decreasing amount of free energy which is available to a Carnot engine in the: Thus the continual march of a thermodynamic system, from lesser to greater entropy, at any given temperature, defines an arrow of time.
It was expected that there was one absolute reference frame, that of the luminiferous aether, in which Maxwell's equations held unmodified in the known form.
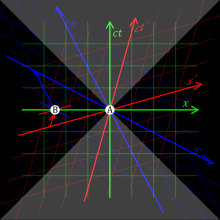
If there is at the point B of space another clock in all respects resembling the one at A, it is possible for an observer at B to determine the time values of events in the immediate neighbourhood of B.
In accordance with definition the two clocks synchronize if We assume that this definition of synchronism is free from contradictions, and possible for any number of points; and that the following relations are universally valid:— Einstein showed that if the speed of light is not changing between reference frames, space and time must be so that the moving observer will measure the same speed of light as the stationary one because velocity is defined by space and time: Indeed, the Lorentz transformation (for two reference frames in relative motion, whose x axis is directed in the direction of the relative velocity)
The speed of light c can be seen as just a conversion factor needed because we measure the dimensions of spacetime in different units; since the metre is currently defined in terms of the second, it has the exact value of 299 792 458 m/s.
We would need a similar factor in Euclidean space if, for example, we measured width in nautical miles and depth in feet.
Employing the metric tensor which describes Minkowski space: Einstein developed a geometric solution to Lorentz's transformation that preserves Maxwell's equations.
According to Einstein's general theory of relativity, a freely moving particle traces a history in spacetime that maximises its proper time.
In an inertial frame, Newton's first law holds; it has its own local geometry, and therefore its own measurements of space and time; there is no 'universal clock'.
The Poisson brackets are superseded by a nonzero commutator, say [H, A] for observable A, and Hamiltonian H: This equation denotes an uncertainty relation in quantum physics.
In 2021 Jun Ye of JILA in Boulder Colorado observed time dilatation in the difference in the rate of optical lattice clock ticks at the top of a cloud of strontium atoms, than at the bottom of that cloud, a column one millimeter tall, under the influence of gravity.
Khemani, Moessner, and Sondhi define a time crystal as a "stable, conservative, macroscopic clock".
In 19th century telegraphy, electrical circuits, some spanning continents and oceans, could transmit codes - simple dots, dashes and spaces.
But it is safe to say that our signalling systems can be only approximately synchronized, a plesiochronous condition, from which jitter need be eliminated.
Additionally, a reference hydrogen maser is also reported to BIPM as a frequency standard for TAI (international atomic time).
But in 1927, Georges Lemaître (1894–1966) argued, on the basis of general relativity, that the universe originated in a primordial explosion.
At the fifth Solvay conference, that year, Einstein brushed him off with "Vos calculs sont corrects, mais votre physique est abominable.
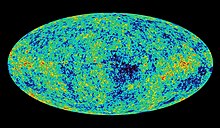
Subsequent experiments arrived at a 2.7 kelvins temperature, corresponding to an age of the universe of 13.8 billion years after the Big Bang.
In our epoch, during which electromagnetic waves can propagate without being disturbed by conductors or charges, we can see the stars, at great distances from us, in the night sky.
(Before this epoch, there was a time, before the universe cooled enough for electrons and nuclei to combine into atoms about 377,000 years after the Big Bang, during which starlight would not have been visible over large distances.)