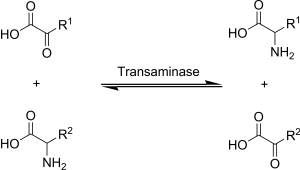
Transamination
α-ketoglutarate acts as the predominant amino-group acceptor and produces glutamate as the new amino acid.
Glutamate's amino group, in turn, is transferred to oxaloacetate in a second transamination reaction yielding aspartate.
For the reaction to complete, aminotransferases require participation of aldehyde containing coenzyme, pyridoxal-5'-phosphate (PLP), a derivative of Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6).
The Schiff base, which is conjugated to the enzyme's pyridinium ring, is the focus of the coenzyme activity.
ISBN 0-471-58589-0 • Gerald Booth "Naphthalene Derivatives" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.