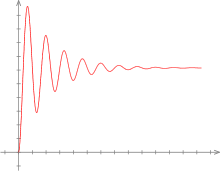
Transient response
[1] It is followed by the steady state response, which is the behavior of the circuit a long time after an external excitation is applied.
It is a transient event preceding the final steady state following a sudden change of a circuit[5] or start-up.
This is generally considered an undesirable effect as it introduces variations in the high and low voltages of a signal, causing instability.
Engineers use voltage regulators and surge protectors to prevent transients in electricity from affecting delicate equipment.
Many such tests administer the induced fast transient oscillation directly, in the form of a damped sine wave, rather than attempting to reproduce the original source.