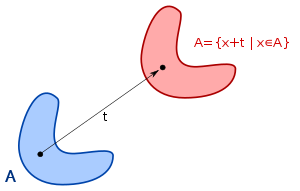
Translational symmetry
if the result after applying A doesn't change if the argument function is translated.
Laws of physics are translationally invariant under a spatial translation if they do not distinguish different points in space.
According to Noether's theorem, space translational symmetry of a physical system is equivalent to the momentum conservation law.
Translational invariance implies that, at least in one direction, the object is infinite: for any given point p, the set of points with the same properties due to the translational symmetry form the infinite discrete set {p + na | n ∈ Z} = p + Z a.
For each set of k independent translation vectors, the symmetry group is isomorphic with Zk.
Different bases of translation vectors generate the same lattice if and only if one is transformed into the other by a matrix of integer coefficients of which the absolute value of the determinant is 1.
In general in 2D, we can take pa + qb and ra + sb for integers p, q, r, and s such that ps − qr is 1 or −1.
Each pair a, b defines a parallelogram, all with the same area, the magnitude of the cross product.
One plane (cross-section) or line, respectively, fully defines the whole object.