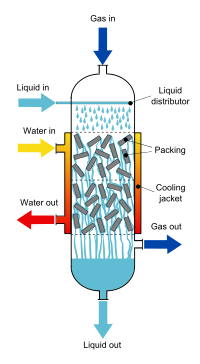
Trickle-bed reactor
A trickle-bed reactor (TBR) is a chemical reactor that uses the downward movement of a liquid and the downward (co-current) or upward (counter-current) movement of gas over a packed bed of (catalyst) particles.
Typical examples are liquid-phase hydrogenation, hydrodesulfurization, and hydrodenitrogenation in refineries (three phase hydrotreater) and oxidation of harmful chemical compounds in wastewater streams or of cumene in the cumene process.
the amount of open literature publications on TBRs is increasing, hinting that the understanding of the hydrodynamics is still limited.
A good introduction to the hydrodynamics of TBR can be found in the classic article by Satterfield.
[2] Rate of reaction and mass transfer equations are derived by Fogler.