Trihalide
A trihalide in chemistry is an organohalide consisting of three halide atoms bonded to a single atom or compound.
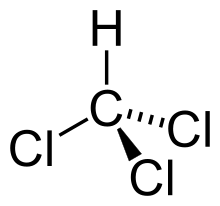
[1][2] An example of a trihalide is chloroform.
The trihalomethanes are the simplest trihalides, because only one hydrogen is connected to the carbon.
The 1,1,1-Trichloroethane is one of the trihalides of ethane.