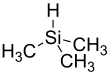
Trimethylsilane
Being a gas, it is less commonly used as a reagent than the related triethylsilane, which is a liquid at room temperature.
Trimethylsilane is used in the semiconductor industry as precursor to deposit dielectrics and barrier layers via plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PE-CVD).
[1] It is also used a source gas to deposit TiSiCN hard coatings via plasma-enhanced magnetron sputtering (PEMS).
It has also been used to deposit silicon carbide hard coatings via low-pressure chemical vapor deposition (LP-CVD) at relatively low temperatures under 1000 °C.
It is an expensive gas but safer to use than silane (SiH4); and produces properties in the coatings that cannot be undertaken by multiple source gases containing silicon and carbon.