Torso
The torso or trunk is an anatomical term for the central part, or the core, of the body of many animals (including human beings), from which the head, neck, limbs, tail and other appendages extend.
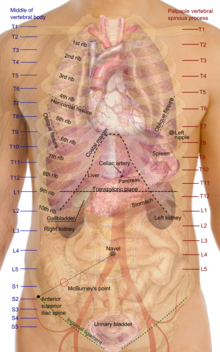
[1] In humans, most critical organs, with the notable exception of the brain, are housed within the torso.
In the upper chest, the heart and lungs are protected by the rib cage, and the abdomen contains most of the organs responsible for digestion: the stomach, which breaks down partially digested food via gastric acid; the liver, which respectively produces bile necessary for digestion; the large and small intestines, which extract nutrients from food; the anus, from which fecal wastes are egested; the rectum, which stores feces; the gallbladder, which stores and concentrates bile; the kidneys, which produce urine, the ureters, which pass it to the bladder for storage; and the urethra, which excretes urine and in a male passes sperm through the seminal vesicles.
Finally, the pelvic region houses both the male and female reproductive organs.
The sensation to the skin is provided by the lateral and dorsal cutaneous branches.