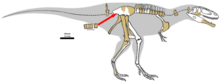
Tyrannotitan
The fossils were found at La Juanita Farm, 28 kilometres (17 mi) northeast of Paso de Indios, Chubut Province, Argentina.
)7, 10, 13, fused sacral centra (5 total), an assortment of distal caudals, ribs, the right femur, a fragmentary left metatarsal 2, pedal phalanges 2-1, 2–2, and 3-3.
The denticles on its teeth are "chisel-like", and are virtually identical to those of other carcharodontosaurids in having a wrinkled enamel surface, heavily serrated mesial and distal carinae, and labiolingually compressed (laterally flattened) crowns.
Characteristics that unite the Giganotosaurini include the presence of a postorbital process on the jugal with a wide base, and a derived femur with a weak fourth trochanter and a shallow broad extensor groove at the distal end.
This region was part of Gondwana and featured a variety of environments, including river systems, floodplains, and semi-arid areas interspersed with scattered forests.
The warm climate and abundant water sources, such as rivers and lakes, supported a diverse ecosystem that included large herbivorous dinosaurs, smaller theropods, and other fauna.
Its diet primarily consisted of large herbivorous dinosaurs such as Chubutisaurus and possibly juveniles or weaker individuals of massive sauropods like Patagotitan.
Evidence suggests that Tyrannotitan may have been an active hunter, using its powerful bite and robust dentition to subdue prey, though it may also have scavenged opportunistically.