Taxation in the United Kingdom
[2] Income tax was announced in Britain by William Pitt the Younger in his budget of December 1798 and introduced in 1799, to pay for weapons and equipment in preparation for the Napoleonic Wars.
The malt tax was easy to collect from brewers; even after it was reduced in 1822, it produced over 10 per cent of government's annual revenues through the 1840s.
Peel, as a Conservative, had opposed income tax in the 1841 general election, but a growing budget deficit required a new source of funds.
The government avoided indirect taxes because they raised the cost of living, and caused discontent among the working class.
The Treasury rejected proposals for a stiff capital levy, which the Labour Party wanted to use to weaken the capitalists.
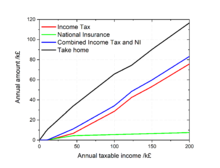
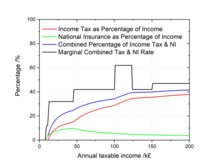
Since 1976 (when it stood at 35%), the basic rate has been reduced by 15%, but this reduction has been largely offset by increases in national insurance contributions and value added tax.
The then opposition Conservative party claimed that this policy caused a decrease in revenue to the Exchequer, by incentivizing tax-avoidance or emigration/offshoring.
They also discuss systemic reasons for the tax falling in the first instance, but say "It is too early to provide a meaningful reassessment of the costing of the reduction.
People who are both resident and domiciled in the United Kingdom are additionally liable to taxation on their worldwide income and gains.
From 6 April 2008, a long-term non-dom (defined as resident in 7 of the previous 9 years) wishing to retain the remittance basis is required to pay an annual tax of £30,000.
[31] The majority of people making use of the non-domiciled tax exemption are wealthy individuals with substantial income from outside of the United Kingdom.
Joint owners can decide how they divide income and expenses,[40][needs update] as long as one does not make a profit and the other a loss.
[43] The coalition government raised this allowance in years following 2014, and the 50% tax bracket was reduced to its current 45% rate.
Certain investments carry a tax favoured status, including: Many holdings and income from them are exempt for "historical reasons".
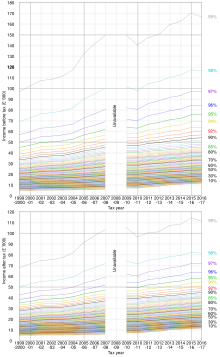
failed to keep up with house price inflation[neutrality is disputed] with the result that some 6 million households currently fall within the scope of inheritance tax.
Recent changes to the tax brought in by the Finance Act 2008 mean that nil-rate bands are transferable between spouses to reduce this burden – something which previously could only be done by setting up complex trusts.
It was introduced in 1993 by the Local Government Finance Act 1992, as a successor to the unpopular Community Charge ("poll tax"), which had (briefly) replaced the Rates system.
In October 2024, Local authorities in England had warned of a potential £54 billion funding shortfall due to rising costs in social care and school transport, according to a report from the County Councils Network (CCN).
[56] The third largest source of government revenues is value added tax (VAT), charged at 20 per cent on supplies of goods and services.
[58] VAT was introduced in 1973, in consequence of Britain's entry to the European Economic Community, at a standard rate of 10 per cent.
[citation needed] On 1 December 2008, VAT was reduced to 15 per cent, as a reaction to the late-2000s recession, by Chancellor Alistair Darling.
[citation needed] On 4 January 2011, VAT was raised to 20 per cent by Chancellor George Osborne, where it remains.
Excise duties are charged on, amongst other things, motor fuel, alcohol, tobacco, betting and vehicles.
Business rates form part of the funding for local government, and are collected by them, but rather than receipts being retained directly they are pooled centrally and then redistributed.
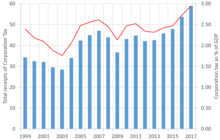
In 2005–06, £19.9 billion was collected in business rates, representing 4.35 per cent of the total United Kingdom tax income.
The rateable value broadly represents the annual rent the property could have been let for on a particular valuation date according to a set of assumptions.
NICs are payable by employees, employers and the self-employed and in the 2010–2011 tax year £96.5 billion was raised, 21.5 per cent of the total collected by HMRC.
On 7 September 2021, Prime Minister Boris Johnson announced that a new tax would be introduced from April 2023 in order to fund the National Health Service backlogs arising as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic and the reform of social care in England.
The aim was to give HMRC time to make the changes required in order for the levy to be introduced.
Companies apply "indexation relief" to the base cost, increasing it in accordance with the Retail Prices Index so that (broadly speaking) the gain is calculated on a post-inflation basis (with different rules apply for gains accrued prior to March 1982).