Ubiquinol
The natural ubiquinol form of coenzyme Q is 2,3-dimethoxy-5-methyl-6-poly prenyl-1,4-benzoquinol, where the polyprenylated side-chain is 9-10 units long in mammals.
An analysis of a range of foods found ubiquinol to be present in 66 out of 70 items and accounted for 46% of the total coenzyme Q10 intake in the Japanese diet.
The reduction of ubiquinone to ubiquinol occurs in Complexes I & II in the electron transfer chain.
The Q cycle[6] is a process that occurs in cytochrome b,[7][8] a component of Complex III in the electron transport chain, and that converts ubiquinol to ubiquinone in a cyclic fashion.
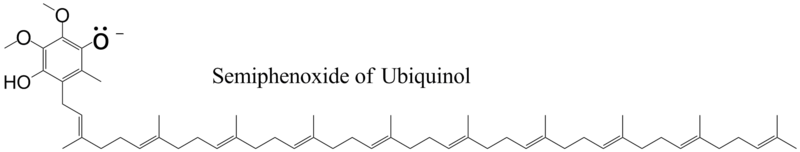
When ubiquinol binds to cytochrome b, the pKa of the phenolic group decreases so that the proton ionizes and the phenoxide anion is formed.