ATX
ATX (Advanced Technology Extended) is a motherboard and power supply configuration specification, patented by David Dent in 1995 at Intel,[1] to improve on previous de facto standards like the AT design.
It was the first major change in desktop computer enclosure, motherboard and power supply design in many years, improving standardization and interchangeability of parts.
In 2004, Intel announced the BTX (Balanced Technology eXtended) standard, intended as a replacement for ATX.
Originally AT style cases had only a keyboard connector and expansion slots for add-on card backplates.
Any other onboard interfaces (such as serial and parallel ports) had to be connected via flying leads to connectors which were mounted either on spaces provided by the case or brackets placed in unused expansion slot positions.
The computer will operate correctly without a plate fitted, although there will be open gaps in the case which may compromise the EMI/RFI screening and allow ingress of dirt and random foreign bodies.
Many power supply cables barely or fail to reach, or are too stiff to make the bend, and extensions are sometimes required due to this placement.
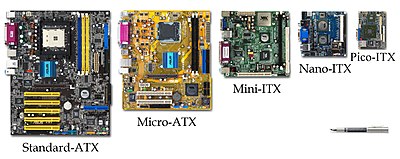
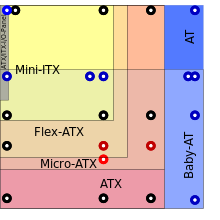
Several ATX-derived designs have been specified that use the same power supply, mountings and basic back panel arrangement, but set different standards for the size of the board and number of expansion slots.
Form factors considered obsolete in 1999 included Baby-AT, full size AT, and the semi-proprietary LPX for low-profile cases.
Proprietary motherboard designs such as those by Compaq, Packard-Bell, Hewlett Packard and others existed, and were not interchangeable with multi-manufacturer boards and cases.
Also unveiled during the January 2008 CES was the Lian Li Armorsuit PC-P80 case with 10 slots designed for the motherboard.
There is a specification for ripple in a 10 Hz–20 MHz bandwidth:[3] The 20–24-pin Molex Mini-Fit Jr. has a power rating of, 9 amperes maximum per pin).
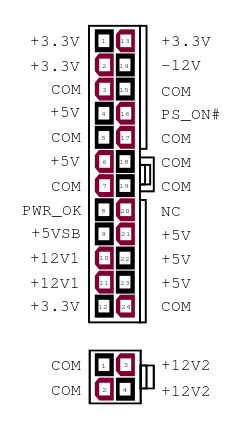
[21] As large server motherboards and 3D graphics cards have required progressively more and more power to operate, it has been necessary to revise and extend the standard beyond the original 20-pin connector, to allow more current using multiple additional pins in parallel.
ATX power supplies generally have the dimensions of 150 × 86 × 140 mm (5.9 × 3.4 × 5.5 in),[22]: 23–24 with the width and height being the same as the preceding LPX (Low Profile eXtension) form factor (which are often incorrectly referred to as "AT" power supplies due to their ubiquitous use in later AT and Baby AT systems, even though the actual AT and Baby AT power supply form factors were physically larger) and share a common mounting layout of four screws arranged on the back side of the unit.
It utilizes a paddle-style DPST switch and is similar to the PC and PC-XT style power supplies.
The general configuration is a double-pole latching mains voltage switch with the four pins connected to wires from a four-core cable.
The new connector also provides a 3.3 volt source, removing the need for motherboards to derive this voltage from the 5 V rail.
[26] This recommendation was removed from later specifications; modern ATX power supplies usually exhaust air from the case.
Also released in March 2005[3] it includes corrections and specifies High Current Series wire terminals for 24-pin ATX motherboard and 4-pin +12 V power connectors.
Higher efficiency generally results in less power consumption (and less waste heat) and the 80% recommendation brings supplies in line with new Energy Star 4.0 mandates.
It added a maximum allowed ripple/noise specification of 400 millivolts to the PWR_ON and PWR_OK signals, requires that the DC power must hold for more than 1 millisecond after the PWR_OK signal drops, clarified country-specific input line harmonic content and electromagnetic compatibility requirements, added a section about Climate Savers, updated recommended power supply configuration charts, and updated the cross-regulation graphs.
Power supply fans are also recommended to turn on with at least a two second delay for an improved user experience.
ATXV12 2.53 makes further recommendations on efficiency and references the Energy Star Computers Specification Version 8.0 which was finalized in April 2020.
[41] Standing for ATX 12-volt-only, this is a new specification published by Intel in 2019, aimed at pre-built systems in the first run, and stricter power efficiency requirements by the California Energy Commission going into effect in 2021.
This greatly simplifies power supplies, but moves DC-to-DC conversion and some connectors to the motherboard instead.
Since −5 V is required only by some ISA-bus expansion cards, this is not an issue with modern hardware and decreases productions costs.
[48] Thin Form Factor is another small power supply design with standard ATX specification connectors.
Although the ATX power supply specifications are mostly vertically compatible in both ways (both electrically and physically), there are potential issues with mixing old motherboards/systems with new PSUs and vice versa.
Climate Savers Computing Initiative promotes energy saving and reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by encouraging development and use of more efficient power supplies.
80 PLUS certifies a variety of efficiency levels for power supplies and encourages their use via financial incentives.