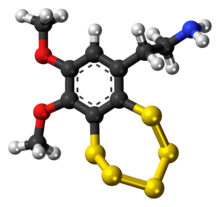
Varacin
Varacin is a bicyclic organosulfur compound originally found in marine Ascidiacea from the Polycitor genus.
[1] It contains an unusual pentathiepin ring which reacts with DNA, and varacin and synthetic analogues have been investigated for their antimicrobial and antitumour properties.
[2][3] Because of its potent biological activity and unusual and challenging ring system, it has been a popular target of efforts toward its total synthesis.
[4][5][6] By virtue of the unsymmetrically substituted benzopentathiepin ring system, varacin and a few related polysulfane natural products exist as potentially isolable enantiomers as a result of planar chirality.
[7] This article about a heterocyclic compound is a stub.