Vegetable
At first, plants that grew locally were cultivated, but as time went on, trade brought common and exotic crops from elsewhere to add to domestic types.
Nowadays, most vegetables are grown all over the world as climate permits, and crops may be cultivated in protected environments in less suitable locations.
The scale of production varies from subsistence farmers supplying the needs of their family for food, to agribusinesses with vast acreages of single-product crops.
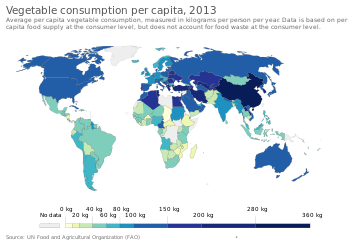
Vegetables can be eaten either raw or cooked and play an important role in human nutrition, being mostly low in fat and carbohydrates, but high in vitamins, minerals and dietary fiber.
[2] The exact definition of "vegetable" may vary simply because of the many parts of a plant consumed as food worldwide—roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds.
The court ruled unanimously in Nix v. Hedden that a tomato is correctly identified as, and thus taxed as, a vegetable, for the purposes of the Tariff of 1883 on imported produce.
[13] Throughout recorded history, the rich have been able to afford a varied diet including meat, vegetables and fruit, but for poor people, meat was a luxury and the food they ate was very dull, typically comprising mainly some staple product made from rice, rye, barley, wheat, millet or maize.
The staple diet of the Aztecs in Central America was maize and they cultivated tomatoes, avocados, beans, peppers, pumpkins, squashes, peanuts, and amaranth seeds to supplement their tortillas and porridge.
[14] In Ancient China, rice was the staple crop in the south and wheat in the north, the latter made into dumplings, noodles, and pancakes.
These were accompanied by a range of vegetables including marrows, broad beans, lentils, onions, leeks, garlic, radishes, and lettuces.
[14] The mainstay of the Ancient Greek diet was bread, and this was accompanied by goat's cheese, olives, figs, fish, and occasionally meat.
[15] In Ancient Rome, a thick porridge was made of emmer wheat or beans, accompanied by green vegetables but little meat, and fish was not esteemed.
Particularly important are the antioxidant vitamins A, C, and E. When vegetables are included in the diet, there is found to be a reduction in the incidence of cancer, stroke, cardiovascular disease, and other chronic ailments.
[35] On a domestic scale, the spade, fork, and hoe are the tools of choice while on commercial farms a range of mechanical equipment is available.
New techniques are changing the cultivation procedures involved in growing vegetables with computer monitoring systems, GPS locators, and self-steer programs for driverless machines giving economic benefits.
Onions and garlic can be dried for a few days in the field and root crops such as potatoes benefit from a short maturation period in warm, moist surroundings, during which time wounds heal and the skin thickens up and hardens.
Before marketing or storage, grading needs to be done to remove damaged goods and select produce according to its quality, size, ripeness, and color.
These losses may be as high as thirty to fifty percent in developing countries where adequate cold storage facilities are not available.
[36] Proper post-harvest storage aimed at extending and ensuring shelf life is best effected by efficient cold chain application.
[38] Cold storage is particularly useful for vegetables such as cauliflower, eggplant, lettuce, radish, spinach, potatoes, and tomatoes, the optimum temperature depending on the type of produce.
[39] The irradiation of vegetables and other agricultural produce by ionizing radiation can be used to preserve it from both microbial infection and insect damage, as well as from physical deterioration.
[41] Canning and freezing are the most commonly used techniques, and vegetables preserved by these methods are generally similar in nutritional value to comparable fresh products with regards to carotenoids, vitamin E, minerals.
The lowest necessary heat and the minimum processing time are used in order to prevent the mechanical breakdown of the product and to preserve the flavor as far as is possible.
The enzyme action will merely be inhibited, and blanching of suitably sized prepared vegetables before freezing mitigates this and prevents off-flavors developing.
[43] Traditionally, sun drying has been used for some products such as tomatoes, mushrooms, and beans, spreading the produce on racks and turning the crop at intervals.
[41] Vinegar is widely used in food preservation; a sufficient concentration of acetic acid prevents the development of destructive micro-organisms, a fact made use of in the preparation of pickles, chutneys and relishes.
Sauerkraut is made from chopped cabbage and relies on lactic acid bacteria which produce compounds that are inhibitory to the growth of other micro-organisms.