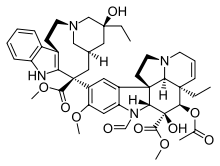
Vinca alkaloid
The Madagascan periwinkle Catharanthus roseus L. is the source for a number of important natural products,[1] including catharanthine and vindoline[2] and the vinca alkaloids it produces from them: leurosine and the chemotherapy agents vinblastine[3] and vincristine,[4] all of which can be obtained from the plant.
[5][6][7][8] The newer semi-synthetic chemotherapeutic agent vinorelbine is used in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer[7][9] and is not known to occur naturally.
[12][11] Anhydrovinblastine is then reacted sequentially with N-bromosuccinimide and trifluoroacetic acid followed by silver tetrafluoroborate to yield vinorelbine.
[13] The vinca alkaloids thus prevent microtubule polymerization, as opposed to the mechanism of action of taxanes.
[14] Minor vinca alkaloids include minovincine, methoxyminovincine, minovincinine, vincadifformine, desoxyvincaminol, and vincamajine.