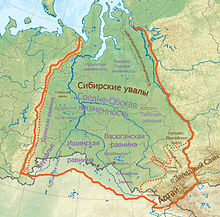
West Siberian Plain
[7] There are salt lakes in the Kulunda Plain, which extends southwards into Kazakhstan and is limited to the south by the Kokshetau Hills.
[8] The West Siberian Plain is very swampy and soils are mostly peaty Histosols and, in the treeless northern part, Histels.
Vasyugan Swamp, one of the world's largest single raised bogs, covers approximately 51,600 square kilometres (19,900 sq mi).
In the south of the plain, where permafrost is largely absent, rich grasslands that are an extension of the Kazakh Steppe formed the original vegetation, which had almost all been cleared by the early 21st century.
A rise of fifty metres in sea level would cause all land between the Arctic Ocean and the Ob-Irtysh confluence near Khanty-Mansiysk to be inundated (see also Turgai Straits, West Siberian Glacial Lake).
It is a region of the Earth's crust that has undergone prolonged subsidence and is composed of horizontal deposits from as much as 65 million years ago.