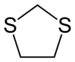
1,3-Dithiolane
Also classified as a heterocycle related cyclopentane by replacing two methylene bridges (-CH2- units) with thioether groups.
[2] Related compounds with the formula R2CS2C2H4 are obtained by condensation of 1,2-ethanedithiol with ketones.
[4] Dithiolanes can often be reverted, i.e., deprotected,[5] to the parent aldehyde and ketone.
[6] 1,3-Dithiolanes derived from aldehydes can be deprotonated: These organolithium compounds degrade with loss of ethylene to give the dthiocarboxylate: In contrast, 2-lithio-1,3-dithianes (RCLiS2C3H6) are long-lived.
1,3-Dithiolanes are susceptible to a variety of degradation processes involving organometallic reagents leading to other organosulfur compounds.