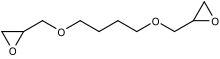
1,4-Butanediol diglycidyl ether
[1] Its main use is in modifying epoxy resins especially viscosity reduction.
1,4-Butanediol and epichlorohydrin are reacted in the presence of a Lewis acid as catalyst to form a halohydrin: each hydroxyl group of the diol reacts with an epoxide on epichlorohydrin.
This process is followed by washing with sodium hydroxide to re-form the epoxide rings in dehydrochlorination reaction.
A key use is modifying the viscosity and properties of epoxy resins[5] which may then be formulated into CASE applications: Coatings,[6] Adhesives, Sealants, Elastomers, composite materials, fillers, putties, plasters, modelling clay and semiconductors.
[12][13] The toxicity is fairly well known and understood and is rated as a severe skin and eye irritant.