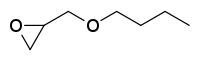
n-Butyl glycidyl ether
[4] n-Butyl alcohol and epichlorohydrin react to form a halohydrin.
This is followed by a caustic dehydrochlorination, to form n-butyl glycidyl ether.
[5][6] Exposure to n-butyl glycidyl ether through inhalation, eye contact, or skin exposure can cause a cough, sore throat, eye and skin redness, and pain.
[9] The use of the diluent does effect mechanical properties and microstructure of epoxy resins.
[10][11] It has been used to simultaneously increase cryogenic strength, ductility and impact resistance of epoxy resins.