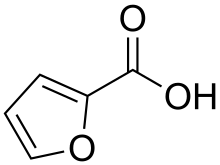
2-Furoic acid
Along with other furans, its name is derived from the Latin word furfur, meaning bran, from which these compounds were first produced.
[3] The compound was first described by Carl Wilhelm Scheele in 1780, who obtained it by the dry distillation of mucic acid.
The current industrial route involves the Cannizaro reaction of furfural in an aqueous NaOH solution.
[12] 2-Furoic acid crystals are highly transparent in the 200–2000 nm wavelength region, are stable up to 130 °C, and generally have low absorption in the UV, visible, and IR ranges.
[13] In optical and dielectric studies, 2-furoic acid crystals may act as paraelectrics in the temperature range < 318 K and ferroelectrics in temperature ranges > 318 K.[14] 2-Furoic acid can be the sole source of carbon and energy for the organism Pseudomonas putida.