Biocatalysis
This has enabled the development of enzymes that can catalyze novel small molecule transformations that may be difficult or impossible using classical synthetic organic chemistry.
-Most enzymes typically function under mild or biological conditions, which minimizes problems of undesired side-reactions such as decomposition, isomerization, racemization and rearrangement, which often plague traditional methodology.
-Through the development of protein engineering, specifically site-directed mutagenesis and directed evolution, enzymes can be modified to enable non-natural reactivity.
This interest in turn is mainly due to the need to synthesize enantiopure compounds as chiral building blocks for Pharmaceutical drugs and agrochemicals.
This mixture can be purified by (I) acylating the amine using an anhydride and then (II) selectively deacylating only the L enantiomer using hog kidney acylase.
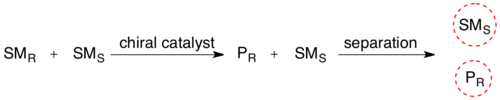
If it is possible to perform such resolutions under conditions where the two substrate- enantiomers are racemizing continuously, all substrate may in theory be converted into enantiopure product.
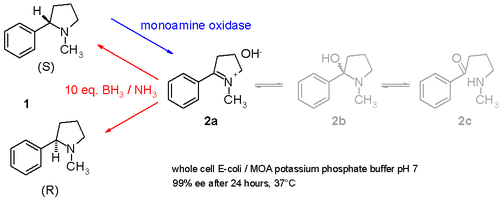
[8] Another study demonstrates how racemic nicotine (mixture of S and R-enantiomers 1 in scheme 3) can be deracemized in a one-pot procedure involving a monoamine oxidase isolated from Aspergillus niger which is able to oxidize only the amine S-enantiomer to the imine 2 and involving an ammonia–borane reducing couple which can reduce the imine 2 back to the amine 1.
Enzymes can provide this chiral environment within the active site and stabilize a particular conformation and favoring formation of one, enantiopure product.
[14] When paired with their respective enzymes (typically ene-reductases) This phenomenon has been utilized by chemists to develop enantioselective reduction methodologies.
For example medium sized lactams can be synthesized in the chiral environment of an ene-reductase through a reductive, baldwin favored, radical cyclization terminated by enantioselective HAT from NADPH.
Many types of PCs with a large range of redox potentials can be utilized, allowing for greater tunability of reactive compared to using a cofactor.
Rose bengal, and external PC, was utilized in tandem with an oxidoreductase to enantioselectively deacylate medium sized alpha-acyl-ketones.