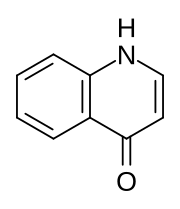
4-Quinolone
It and 2-quinolone are the two most important parent (meaning simplified) quinolones.
4-Quinolone exists in equilibrium with a minor tautomer, 4-hydroxyquinoline (CAS#611-36-9).
Aside from pedagogical interest, 4-quinolone is of little intrinsic value but its derivatives, the 4-quinolone antibiotics, represent a large class of important drugs.
[1] The chemical synthesis of quinolones often involves ring-closing reactions.
An example of such a synthesis is the Camps cyclization, which, depending on starting materials and reaction conditions, can give both 2-hydroxyquinolines (B) and 4-hydroxyquinolines (A) as shown.