5-Bromouracil
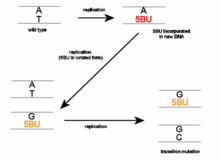
The keto form (shown in the infobox) is complementary to adenine, so it can be incorporated into DNA by aligning opposite adenine residues during DNA replication (see below left).
The three forms frequently interchange so base-pairing properties can become altered at any time.
The result of this is that during a subsequent round of replication a different base is aligned opposite the 5-BrU residue.
Further rounds of replication 'fix' the change by incorporating a normal nitrogen base into the complementary strand.
This base pair will change from an A-T to a G-C or from a G-C to an A-T after a number of replication cycles, depending on whether 5-BrU is within the DNA molecule or is an incoming base when it is enolized or ionized.