Film capacitor
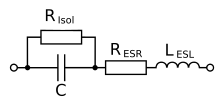
The setup behaves like a large number of individual capacitors connected in parallel, thus reducing the internal ohmic losses (ESR) and the parasitic inductance (ESL).
[12] This property of self-healing allows the use of a single-layer winding of metallized films without any additional protection against defects, and thereby leads to a reduction in the amount of the physical space required to achieve a given performance specification.
Typically, after slitting the metallized film to the desired width, any resulting defects can be burned out (healed) by applying a suitable voltage before winding.
Therefore, the area affected is limited and the fault is gently controlled, significantly reducing internal damage to the capacitor, which can thus remain in service with only an infinitesimal reduction in capacitance.
This capability depends on all internal connections of the film capacitor withstanding the peak current loads up to the maximum specified temperature.
This design also halves the total self-inductance of the capacitor, because in effect, two inductors are connected in parallel, which allows less-unimpeded passage of faster pulses (higher so-called "dV/dt" rating).
With the development of plastic materials by organic chemists during the Second World War, the capacitor industry began to replace paper with thinner polymer films.
German manufacturers such as WIMA, Roederstein, Siemens and Philips were trend-setters and leaders in a world market driven by consumer electronics.
Additionally, most plastics are subject to fewer chemical changes over long periods, providing long-term stability of their electrical parameters.
The polar insulating dielectric cellulose acetate was a synthetic resin that could be made for metallized capacitors in paint film thickness down to about 3 μm.
The most important advantages of film capacitors are the stability of their electrical values over long durations, their reliability, and lower cost than some other types for the same applications.
The reason for this is that the mass quantities required by the market for film caps are quite small compared to typical chemical company production runs.
They are divided into different temperature coefficient grades (α) with associated tolerances and preferred values of permissible change of capacitance after mechanical, ambient (moisture) and life time tests.
[33] The low cost of polyester and the relatively compact dimensions are the main reasons for the high prevalence of PET film capacitors in modern designs.
The better adhering of metallization on paper is advantageous especially at high current pulse loads, and the polypropylene film dielectric increases the voltage rating.
[50] Thermoplastic polymers such as Polyimide (PI), Polyamide (PA, better known as Nylon or Perlon), Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), Siloxane, Polysulfone (PEx) and Aromatic Polyester (FPE) are described in the technical literature as possible dielectric films for capacitors.
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) has a very high permittivity of 18 to 20, which allows large amounts of energy to be stored in a small space (volumetric efficiency).
The manufacturers Wima, Vishay and TDK Epcos specify the electrical parameters of their film capacitors in a general technical information sheet.
The rated AC voltage is generally calculated so that an internal temperature rise of 8 to 10 K sets the allowed limit for film capacitors.
Manufacturers also adopt cheaper and smaller construction intended to avoid corona effect without series-connected sections, for example minimising enclosed air.
The maximum permissible pulse rise time of film capacitors which may be applied within the rated temperature range is specified in the relevant data sheets.
While the frequency- and temperature-dependencies arise directly from physical laws, the time dependence is related to aging and moisture adsorption processes.
This more expensive fabrication processing may account for the fact that film capacitors with the same basic body design can be supplied in different life time stability ratings called Performance grades.
The permissible changes of capacitance, dissipation factor and insulation resistance vary with the film material, and are specified in the relevant data sheet.
Film capacitors generally are very reliable components with very low failure rates, with predicted life expectancies of decades under normal conditions.
Tight capacitance tolerances are required for timing applications in signal lights or pulse width generators to control the speed of motors, PP film capacitors are also well-suited because of their very low leakage current.
For similar reasons, PP film capacitors, often in versions with special terminals for high peak currents, work well as snubbers for power electronic circuits.
Film capacitors made with lower-cost plastics are used for non-critical applications which do not require ultra-stable characteristics over a wide temperature range, such as for smoothing or AC signal coupling.
Specially widened terminals which can be mounted directly beneath semiconductor packages can help to increase current handling and decrease inductance.
The most popular simple snubber circuit consists out of a film capacitor and a resistor in series, connected in parallel with a semiconductor component to suppress or damp undesirable voltage spikes.