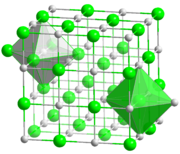
Alkali metal halide
Caesium chloride, bromide, and iodide crystallize in a body-centered cubic lattice that accommodates coordination number of eight for the larger metal cation (and the anion also).
[2] The alkali metal halides exist as colourless crystalline solids, although as finely ground powders appear white.
At still higher temperatures, these liquids evaporate to give gases composed of diatomic molecules.
These compounds dissolve in polar solvents to give ionic solutions that contain highly solvated anions and cations.
The numbers beside the compounds show the electronegativity difference between the elements based on the Pauling scale.